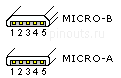
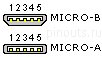
While many currently available devices and cables still use Mini-USB plugs, the Micro-USB connectors are widely adopted and most widely used. The thinner micro connectors replaced the Mini plugs in new devices including smartphones, personal digital assistants, and cameras. The cellular phone carrier group, Open Mobile Terminal Platform (OMTP) endorsed Micro-USB as the standard connector for data and power on mobile devices, and in 2009 it was accepted by almost all cell phone manufacturers as the standard charging port. Nowdays Micro-USB connector start to superseed by USB type-C connector.
| Pin | Name | Cable color | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | VCC | Red | +5 VDC |
| 2 | D- | White | Data - |
| 3 | D+ | Green | Data + |
| 4 | ID | May be N/C, GND or used as an attached device presence indicator (shorted to GND with resistor) | |
| 5 | GND | Black | Ground |
USB pinout signals
USB is a serial bus. It uses 4 shielded wires: two for power (+5v & GND) and two for differential data signals (labelled as D+ and D- in pinout). NRZI (Non Return to Zero Invert) encoding scheme used to send data with a sync field to synchronise the host and receiver clocks. In USB data cable Data+ and Data- signals are transmitted on a twisted pair. No termination needed. Half-duplex differential signaling helps to combat the effects of electromagnetic noise on longer lines. Contrary to popular belief, D+ and D- operate together; they are not separate simplex connections.


 correct
correct incorrect
incorrect